Help
Functoid Definitions
Help menu
- Help content
- AS2
- Examples and Tutorials
- IO Queues and Forms
- Maps
- Schemas
- Send and Receive Ports
- Send and Receive Ports / Transports
- Servers
- Static Configuration
- Tracking
- Workflows
- Workflows / Workflow Activities
- Call Web Service Direct Activity
- Compensatable Sequence Activity
- Compensatable Transaction Scope Activity
- Compensate Activity
- Conditioned Activity Group
- Database Activity
- Delay Activity
- Event Handling Scope Activity
- Event Driven Activity
- Expression Activity
- Fault Handler Activity
- If Else Activity
- Increment Activity
- Invoke Web Service Activity
- Invoke Blue Integrator Workflow Activity
- Invoke Workflow Activity
- Listen Activity
- Map Activity
- Parallel Activity
- Policy Activity
- Send Receive Port Response Activity
- Replicator Activity
- Send Receive Port Response Activity
- Send Port Message Activity
- Sequence Activity
- Suspend Activity
- Synchronization Scope Activity
- Transaction Scope Activity
- While Activity
Advanced Functoids
Call Nested map
Function
Allows you to call another map from within a map (ideal for breaking down a complex map into separate tasks).
Use
Specify the map to be called, and any more parameters; the first parameter is the source document to the map being called. Any other parameters can be embedded in parameter values using {1} to {10} syntax, for additional parameters 1 to 10.
Call Nested XML
Function
Allows you to call another map from within a map, but assumes the input and output to the map being called are both in Xml format.
Use
Specify the map to be called, and any more parameters; the first parameter is the source document to the map being called. Any other parameters can be embedded in parameter values using {1} to {10} syntax, for additional parameters 1 to 10.
Code Functoid
Function
Allows custom C# or VB.Net Visual Studio for Applications code to be executed.
Use
Double click to edit the properties, then enter a function name, click OK and the VSTA editor is launched allowing you to enter custom code. You can edit the generated function to take appropriate parameters and return required values.
![]() NOTE You can debug Code Functoids, by simply using the Debug | Start menu option in Visual Studio for Applications.
NOTE You can debug Code Functoids, by simply using the Debug | Start menu option in Visual Studio for Applications.
Collection Accessor
Function
Allows an item from a System.Collections based object to be accessed.
Use
Accesses an item from a collection, using the second parameter as the index ( 1 based ).
Collection Enumerator
Function
To iterate through any collection, and fire an output value once per item in the collection.
Use
The collection parameter (the only parameter) can be any object implementing IEnumerable. Ideal for retrieving the contents of an array individually.
Count
Function
Counts all scoped instances of the parameter link.
Use
Returns the current numeric count of all scoped instances of the parameter link. This differs from the Cumulative Count functoid, which returns the final rather than current count.
Default Value Functoid
Function
Replaces an empty or null value with a default value.
Use
The Default Value Functoid allows you to specify a default value to replace any empty or null value. Null values are returned from certain functoids to indicate the absence of a result, whereas empty values are valid but empty strings. In the absence of a Default Value Functoid, null values will not generally be propagated through the map.
Duplicate Suppress
Function
Removes duplicate values leaving only unique values.
Use
This Functoid only allows unique values (within any specified scope, or the Page scope by default) through by suppressing any parameter value it has ‘seen’ before.
Multi-Channel Collection Enumerator
Function
Iterates through multiple collections, firing an output value once per item in each collection.
Use
Has the same effect as the Collection Enumerator functoid, except it may have multiple input parameters and will iterate through each of them.
Multi-Channel Enumerator Channel Select
Function
Selects a channel from a Multi-Channel Enumerator output.
Use
The first parameter is the array object, the second is the channel index (starting from one)
Passive Value Functoid
Function
Prevents a functoid from being active, and thus automatically creating an output value.
Use
The Passive Value Functoid can be used to remove the active attribute of a value, such that it will no longer force the creation of the output node to which it connects. Thus the value specified through a Passive Value Functoid will only be used if something else causes the relevant output node to be created. Passive Value Functoids can be used to minimize If / Then logic in Maps.
Value Change
Function
Suppresses any successive outputs of the same value.
Use
This Functoid pushes an active value out only if the value is different to any previous value. With sorted, flattened input this thus allows the creation of structured output by triggering new Xml output grouping elements when values change. An example of this is below.
Suppose you have input data on telephone numbers, in the following format:
Contact ID
1
1
2
3
3
Telephone
09673 372813
012 233 7281
09633 422813
013 232 4923
08633 2932323
Constant Functoids
Constant
Function
Provides a constant value.Use
The Constant Functoid allows you to specify a constant value as output, and is used to populate fixed values, for example a customer reference number when creating a supplier order. This Functoid takes no parameters – you specify the constant value via its’ properties form as shown below.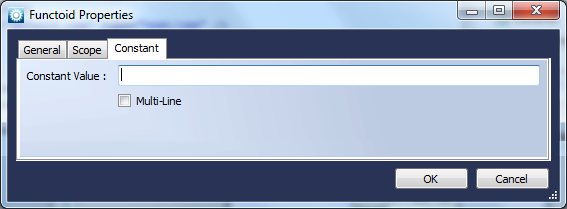
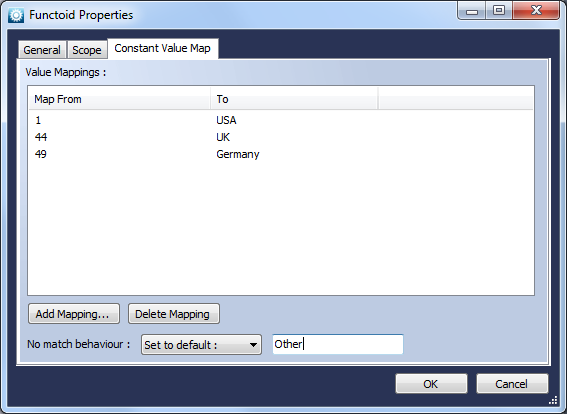
Constant Value Map
Function
Maps a constant value to another.
Use
The Constant Value Map allows you to add a number of mappings from constant value to constant value.). This can be useful in tidying up excess if/then/else logic. The parameters can be of any type, although are compared as strings. If a match is not found, there are four options to choose from:
- Fail: throw an exception
- Return null: null is returned instead of a constant
- Suppress output: nothing is returned
- Set to default: a specified value is returned
Below is the Constant Value Map Properties window, with the Constant Value Map tab selected.
Cumulative Functoids
Convert to Integer
Function
Turns the specified string or object into an integer.Use
The Convert to Integer Functoid takes an input parameter and converts it to an integer, default value 0 if the value cannot be converted. Floating point values are rounded down.Is Number
Function
Checks the given value is a number.Use
This Functoid takes a single argument, and returns true or false depending on whether the given argument is numeric (or can be converted to numeric) or not.Concatenate
Function
Returns the string concatenation of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
All instances of the parameter link are appended together into a single string.Count Distinct
Function
Returns the numeric count of all distinct scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
All the distinct instances of the parameter link are counted, returning an integral total.Count
Function
Returns the numeric count of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
All the scoped instances of the parameter link are counted, returning an integral total.First
Function
Returns the first scoped instance of the parameter link.Use
The first scoped instance of the parameter link is returned. Any following instances are ignored.Last
Function
Returns the last scoped instance of the parameter link.Use
The last scoped instance of the parameter link is returned. Previous instances are ignored.Maximum String
Function
Returns the string maximum of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
Compares all scoped instances of the parameter link, and returns the string maximum.Maximum
Function
Returns the numeric maximum of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
Compares all scoped instances of the parameter link, and returns the maximum.Mean
Function
Returns the numeric mean (average) of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
Compares all scoped instances of the parameter link, and returns the average.Minimum String
Function
Returns the string minimum of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
Compares all scoped instances of the parameter link, and returns the maximum.Minimum
Function
Returns the numeric minimum of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
Compares all scoped instances of the parameter link, and returns the minimum.Sum
Function
Returns the numeric sum of all scoped instances of the parameter link.Use
Adds all scoped instances of the parameter link together and returns the total.Database / Table Functoids
Database Table Functoid
Function
A functoid that executes a SQL statement to return a Data Table.Use
The Database Functoid allows you to specify a database connection and a query (which can have token replacements from Functoid parameters), and returns a DataSet (System.Data.DataSet) which can then be further processed by other Functoids, typically the DataSetTableSelector.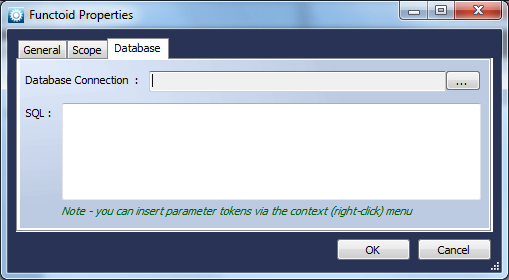
The database connection and query template of the Database Functoid are configured via a Properties page, which can be viewed by double-clicking. Token parameters are added by dragging them into the left of the Functoid, as normal.
Database Value Functoid
Function
Retrieves a value from a database.
Use
The Database Value Functoid allows you to look up a value from a database directly.
DataRow Field Extractor
Function
Returns a Data Value field from a DataRow (System.Data.DataRow).
Use
Allows the selection of a Data Value from a DataRow (System.Data.DataRow) by providing a name or index in the second parameter. Typically the DataRow would have been returned by a TableRowEnumerator or TableRowExtractor Functoid.
DataSet Table Selector
Function
Selects a Table (System.Data.DataTable) from a DataSet (System.Data.DataSet).
Use
Allows the selection of a Table (System.Data.DataTable) from a DataSet (System.Data.DataSet) by providing the table name in the second parameter.
Make Table
Function
Creates a table by logically grouping the input parameters.
Use
The functoid structures all of the input parameters into a table, allowing a lookup by row and column.
Drag the incoming links to the Functoid, double click to edit the Functoid properties, set the number of rows and columns, and for each cell in the table specify either a fixed value or select an incoming link.
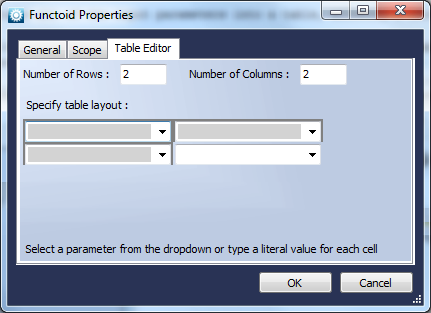
Table Lookup
Function
Extracts a value out of the given System.Data.DataTable.
Use
This Functoid allows you to extract a value from a DataTable, by specifying a DataTable, a Key (first column) value, and the name of the column for which you want to extract the value. null is returned if no matching value is found.
Table Row Count
Function
Returns the count of rows in the given table (System.Data.DataTable).
Use
This Functoid returns the count of rows in the specified DataTable.
Table Row Enumerator
Function
Enumerates the rows in a table.
Use
This Functoid enumerates the rows in a DataTable, firing an output DataRow for each (which can in turn be used by a DataRowFieldExtractor Functoid).
Table Row Extractor
Function
Returns the given row of the System.Data.DataTable (1-based).
Use
This Functoid extracts a row from a DataTable by index (1-based – i.e. the first record is 1). It takes two parameters, the DataTable (typically obtained from another Database Functoid) and the index.
Date / Time Comparison Functoids
Equals
Function
Compares two date/times for equality.
Use
Compares two date/time parameters and returns true if they are equal.
Greater than or Equals
Function
Compares two date/times for one being great than or equal to the other.
Use
Compares two date/time parameters and returns true if they are equal or if the first is later.
Greater Than
Function
Compares two date/times for one being greater than the other.
Use
Compares two date/time parameters and returns true if the first is later.
Less than or Equals
Function
Compares two date/times for one being less than or equal to the other.
Use
Compares two date/time parameters and returns true if they are equal or if the first is earlier.
Less than
Function
Compares two date/times for one being less than the other.
Use
Compares two date/time parameters and returns true if the first is earlier.
Not Equals
Function
Compares two date/times for inequality.
Use
Compares two date/time parameters and returns true if they are not equal.
Date / Time Functoids
Date Add
Function
Adds an offset to a Date/Time.
Use
A quantity (second parameter) is added to a date (first parameter). An optional time unit (y,mo,d,h,mi,s,ms) can be provided in a third parameter.
Date Difference
Function
Calculates the difference between two Date/Times.
Use
Calculates the difference between two Date/Times, as a floating point number if a Time unit is provided, otherwise as a System.TimSpan.
Date/Time Format
Function
Formats a Date/Time into string format.
Use
An explicit date/time format string can be provided in a second parameter, (in .Net format).
Date/Time Parse
Function
Parses a Date/Time from string format into a System.DateTime value.
Use
This functoid does the reverse of DateTimeFormat, again using a format string in a second parameter. See above.
Now (Date)
Function
Returns the current date.
Use
Returns the current date as a System.DateTime.
Now (Date/Time)
Function
Returns the current date/time.
Use
Returns the current date and time as a System.DateTime.
Now (Time)
Function
Returns the current time.
Use
Returns the current time as a System.TimeSpan.
Time Add
Function
Adds an offset to a Time.
Use
A quantity (second parameter) is added to a time (first parameter). An optional time unit (h,mi,s,ms) can be provided in a third parameter.
Time Parse
Function
Parses a Time from a string.
Use
Parses a Time from string format into a System.TimeSpan value.
HL/7 Functoids
HL/7 ACK
Function
Creates a HL/7 v2.x ACK message.
Use
The functoid takes a string message and two optional boolean flags. The first to indicate whether to acknowledge success or failure (default = success), the second to indicate of any additional freetext information to specify (v3 only).
Logical Functoids
AND
Function
The logical AND of the input conditions.
Use
Returns true if all the boolean parameters are true. Otherwise returns false.
EXISTS
Function
Checks the given value/node exists.
Use
Returns true if the given value/node is not null.
EXISTS and not empty
Function
Checks the given value/node exists and is not empty
Use
Returns true only if the given value/node is not null and is not empty.
NOT
Function
The logical NOT of the input condition.
Use
Returns the inverse of a boolean parameter. i.e. true returns false, false returns true.
OR
Function
The logical OR of the input conditions.
Use
Returns true if any of the two or more parameters are true.
Flow Control Functoids
If/Then/Else
Function
If/Then/Else logic.
Use
This Functoid allows you to specify a condition and one or two alternate values. If the condition equates to true, the first value is returned from the Functoid. If the value is false, the second value will be returned (or if no second value was specified there will be no output value).
The condition can be in the form of the output of a logical or comparison Functoid, or it can be a scope, or it can be convertible to a string – in which case it will be false if it is empty, null, 0, or any established English representation of false and otherwise true.
If/Then
Function
If/Then logic.
Use
If the first boolean parameter is true, the second parameter is returned, if false it isn’t.
Conditional Go
Function
Conditionally allows data passing through a link.
Use
The Conditional Go functoid stops data passing through a link unless the specified condition is met. It is different to the If / Then functoid as instead of propagating a null value if the condition is not met, it gives no output at all.
Conditional Stop
Function
Conditionally stops data passing through a link.
Use
The Conditional Stop functoid stops data passing through a link if the specified condition is met.
Conditional Stop If Null Or Empty
Function
Stops null or empty values passing through a link .
Use
The functoid stops data passing through a link if it is either null or is empty.
Numeric Comparison Functoids
Equals
Function
Compares two or more numbers for equality.
Use
Returns true if all the numeric parameters are equal.
Greater than or Equal
Function
Compares two numbers for difference and equality.
Use
Compares two numeric parameters and returns true if they are equal or if the first has the greater value.
Greater Than
Function
Compares two numbers for difference.
Use
Compares two numeric parameters and returns true if the first has the greater value.
Less than or Equal
Function
Compares two numbers for negative difference and equality.
Use
Compares two numeric parameters and returns true if they are equal or if the first has the lesser value.
Less than
Function
Compares two numbers for negative difference.
Use
Compares two numeric parameters and returns true if the first has the lesser value.
Not Equal
Function
Compares two numbers for inequality.
Use
Compares two numeric parameters and returns true if their value’s differ.
Between
Function
Determines whether a value lies between two numbers inclusively.
Use
Returns true if the parameter is greater or equal to the lower boundary and less than or equal to the upper boundary.
Numeric Functoids
Abs
Function
Returns the absolute value of a number.
Use
If a numeric parameter is negative, this functoid changes the sign to positive. Positive parameters are returned unchanged.
Add Percent
Function
Adds the specified percentage to the given number.
Use
The second parameter is the percentage, which is added to the value in the first parameter.
Add
Function
Adds numbers together.
Use
Adds two or more numeric parameters together and returns the total.
Divide
Function
Divides one number by another.
Use
Divides the first numeric parameter by the second numeric parameter and returns the result.
Log
Function
Returns the power 10 log of the given number.
Use
Returns the power 10 log of the given number so that if the parameter is x and the returned value is y, x= 10y
Maximum
Function
Returns the maximum of a set of numbers.
Use
Compares two or more numeric parameters and returns the parameter of greatest value.
Minimum
Function
Returns the minimum of a set of numbers.
Use
Compares two or more numeric parameters and returns the parameter of least value.
Multiply
Function
Multiplies numbers together.
Use
Multiplies two or more numeric parameters together and returns the product.
Power
Function
Raises one number to the power of another.
Use
The first parameter is the base, the second the power. The result is returned.
Remainder
Function
Returns the integer remainder after dividing one number by another.
Use
Divides the first numeric parameter (dividend) by the second numeric parameter (divisor) and returns the difference between the integral result (quotient), and the first parameter (dividend).
Square Root
Function
Returns the square root of the given number.
Use
Returns the square root of the numeric parameter such that param = result * result
Subtract
Function
Subtracts one number from another.
Use
Returns the result of the first parameter minus the second.
String Comparison Functoids
Equals
Function
Compares two strings for equality.
Use
Compares two string parameters and returns true if they are equal. If an optional third boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.
Greater than or Equals
Function
Compares two strings for difference and equality.
Use
Compares two string parameters and returns true if they are equal or if the first is alphabetically later. If an optional third boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.
Greater Than
Function
Compares two strings for difference.
Use
Compares two string parameters and returns true if the first is alphabetically later. If an optional third boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.
Less than or Equals
Function
Compares two strings for negative difference and equality.
Use
Compares two string parameters and returns true if they are equal or if the first is alphabetically earlier. If an optional third boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.
Less than
Function
Compares two strings for negative difference.
Use
Compares two string parameters and returns true if the first is alphabetically earlier. If an optional third boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.
Not Equal
Function
Compares two strings for inequality.
Use
Compares two string parameters and returns true if they are not equal. If an optional third boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.
String Functoids
Concatenate
Function
Concatenates strings together.
Use
Appends two or more strings together in parameter order, and returns the combined string.
First Word
Function
Extracts the first word of the specified string.
Use
Returns the sequence of characters before the first TAB or SPACE.
Last Word
Function
Extracts the last word of the specified string.
Use
Returns the last sequence of characters after the final TAB or SPACE.
Length
Function
Returns the length of the given string.
Use
Returns the length of the string parameter.
Pad
Function
Pads the given string to a minimum number of characters.
Use
Pads a given string (first parameter) to a minimum set size (second parameter). An optional (third parameter) padding character can be specified. If one isn’t SPACE is used. A boolean (fourth parameter) can be optionally specified; if true or 1, the string is padded on the right side, otherwise it is padded on the left.
Split
Function
Splits a string at a separator.
Use
Splits a string according to an optionally supplied separator. A comma or newline is used if a separator isn’t supplied.
String Find
Function
Searches for an instance of a substring within a string.
Use
Finds an instance of the second string specified in the first string, and returns its’ index (0 if not found, 1 is the index of the first character)
String Format
Function
Forms a tokenized string.
Use
Forms a tokenized string from an optional number of parameter tokens. The format string is specified in the properties window as shown below.
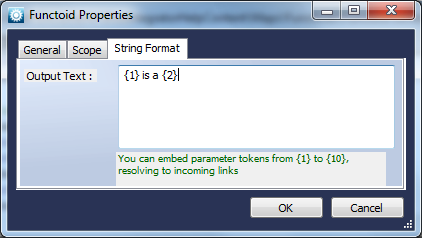
String Replace
Function
Replaces all instances of a string with another.Use
Replaces all instances of the second string parameter in the first string parameter with the replacement third string parameter. If an optional forth boolean parameter is true, the comparison is case sensitive. Otherwise the case is ignored.Substring
Function
Extracts a substring from a string.Use
An input string, index, and length parameter (in that order) are provided and a substring starting at the index (from 1) and of specified length is extracted from the input string.To Lower
Function
Turns a string to lower case.Use
Returns the specified string parameter in lower case.To NameCase
Function
Turns a string to name-case.Use
Returns the specified string parameter in name-case; the first character of each word is capitalized, the rest are in lower case.To Upper
Function
Turns a string to upper case.Use
Returns the specified string parameter in upper case.Trim
Function
Trims a specified string of whitespace.Use
Trims the specified string parameter of leading and trailing whitespace.XML Functoids
Deep Copy
Function
Copies an XML element, with all child elements and attributes.Use
This Functoid copies a complete tree from the source document to a similar tree in the destination document – that is including the complete child structure. This can be particularly useful when using ‘Any’ schema elements.Literal XML
Function
Allows literal XML to be specified.Use
This Functoid allows you, via its’ properties page accessible by double-clicking, to specify a literal Xml document which can then be passed as parameter to other Xml related Functoids including the XPathExpression and XslTransformation ones.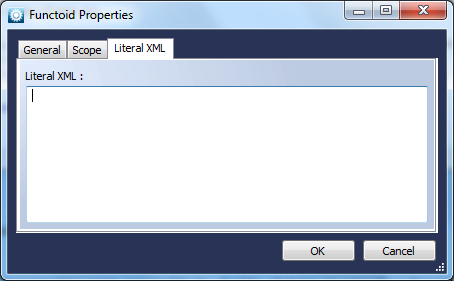
Merge XML
Function
Merges two Xml documents, by appending the records under the root element.Use
The Merge Xml Functoid takes two Xml documents, and merges them together. Effectively all child-nodes of the root of the second document are added to the root of the first document.XPath Expression
Function
Allows execution of an Xpath expression on either a given document node (if specified) or the whole document (if no parameters are specified).Use
This Functoid allows you to execute an XPath expression, which can include tokens corresponding to parameters. It takes an XML Document as parameter, plus up to 10 parameter tokens. The XPath expression is configured via its’ properties form, which can be obtained by double-clicking, and includes a link to embed tokens in the expression, thus allowing dynamic lookup.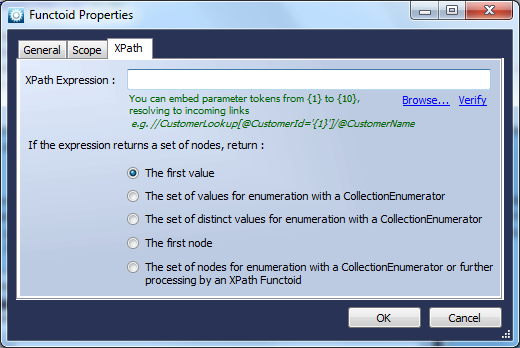
XSL Transformation
Function
Allows execution of an XSL stylesheet on either a given document node (if specified) or the whole document (if no parameters are specified).Use
This Functoid allows you to execute an Xsl transformation on an Xml document. The Xsl is configured via the properties form, launched by double-clicking. The Xml document is taken as parameter.